Lifestyle
Scientists Decode Ancient DNA to Reveal Napoleon’s Troops’ Illnesses
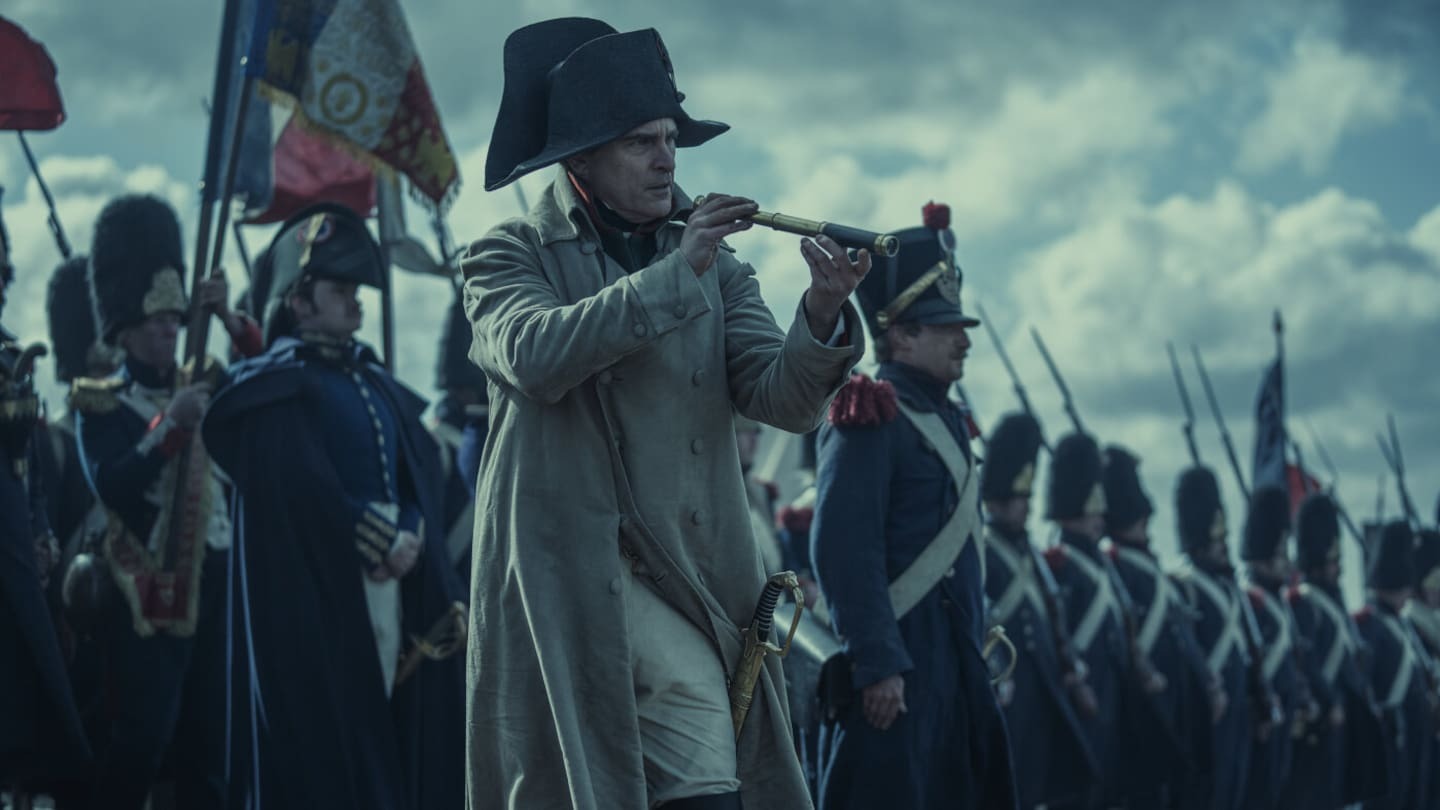

Research published in the journal Current Biology sheds light on the diseases that devastated Napoleon Bonaparte’s army during the ill-fated invasion of Russia in 1812. By examining ancient DNA preserved in the teeth of 13 soldiers, scientists have identified two additional pathogens—paratyphoid fever and relapsing fever—that contributed to the substantial loss of life. This new evidence complements historical accounts that primarily attributed the army’s decline to typhus, a louse-borne disease.
In the summer of 1812, Emperor Napoleon led a massive force of approximately 500,000 troops into Russia, where they faced a harsh retreat. The Russian military employed scorched-earth tactics, leaving behind devastated lands. By autumn, an estimated 300,000 soldiers succumbed not only to military confrontations but also to illness, extreme cold, starvation, and exhaustion.
Discovery of New Pathogens
The study, conducted by researchers at Institut Pasteur, analyzed bacterial DNA fragments found in the dental remains of soldiers interred in a mass grave in Lithuania. This site, unearthed in 2001, contained the remains of over 3,000 of Napoleon’s troops. Previous investigations had focused primarily on the presence of Rickettsia prowazekii, the bacteria responsible for typhus.
In this latest research, scientists employed advanced gene-sequencing techniques to examine the microbial DNA comprehensively. They discovered fragments of Salmonella enterica, which can cause paratyphoid fever, and Borrelia recurrentis, known to cause relapsing fever. These findings suggest that the soldiers were afflicted by multiple infections, a reality that aligns with historical descriptions of the dire conditions faced by the troops.
Remi Barbieri, a postdoctoral researcher at Institut Pasteur, emphasized that the study does not negate the presence of typhus but rather illustrates a more complex picture of the health crises affecting Napoleon’s army. “It’s not surprising that such a large army, covering so much ground in such terrible conditions, would suffer from other illnesses,” he remarked.
Historical Context and Impact
The conditions surrounding the burial of these soldiers were grim. Excavations revealed that the bodies had been hastily thrown into a trench, with horse skeletons found alongside human remains. Evidence suggested that many bodies were frozen in the positions they died, highlighting the severe conditions faced during the winter months of 1812.
In addition to the newly identified pathogens, the study reflects on the historical context provided by medical reports from that time. One such document by army physician J.R.L. de Kirckhoff described gastrointestinal distress attributed to contaminated food, specifically mentioning “large barrels of salted beets” consumed by the troops. These details offer insight into the multifaceted health challenges that contributed to the catastrophic losses experienced by Napoleon’s forces.
The implications of this research extend beyond historical curiosity. It showcases the advancements in microbial genetics, which have revolutionized our understanding of diseases and their evolution. As Anne Stone, an anthropological geneticist at Arizona State University, noted, the study employs modern techniques to analyze ancient samples, providing a clearer picture of the past.
This research not only enriches the narrative of Napoleon’s failed campaign but also serves as a reminder of the vulnerabilities faced by armies throughout history, particularly in the absence of modern medical advancements. As historian and author Stephan Talty pointed out, the findings reinforce the notion that the invasion was doomed from the start, exacerbated by the limitations of the time.
The study opens new avenues for understanding how historical events are shaped by health crises, deepening the narrative of one of the most notorious military campaigns in history.
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoPrivate Funeral Held for Dean Field and His Three Children
-

 Top Stories3 weeks ago
Top Stories3 weeks agoFuneral Planned for Field Siblings After Tragic House Fire
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoNetball New Zealand Stands Down Dame Noeline Taurua for Series
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoTributes Pour In for Lachlan Rofe, Reality Star, Dead at 47
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoNew ‘Maverick’ Chaser Joins Beat the Chasers Season Finale
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoSilver Ferns Legend Laura Langman Criticizes Team’s Attitude
-

 Sports1 month ago
Sports1 month agoEli Katoa Rushed to Hospital After Sideline Incident During Match
-

 World4 weeks ago
World4 weeks agoInvestigation Underway in Tragic Sanson House Fire Involving Family
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoNetball NZ Calls for Respect Amid Dame Taurua’s Standoff
-

 Top Stories3 weeks ago
Top Stories3 weeks agoShock and Grief Follow Tragic Family Deaths in New Zealand
-
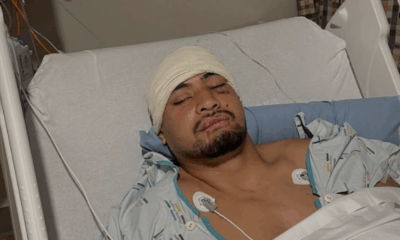
 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoEli Katoa Shares Positive Recovery Update After Brain Surgery
-

 Entertainment4 months ago
Entertainment4 months agoKhloe Kardashian Embraces Innovative Stem Cell Therapy in Mexico





















