Politics
Indian Court Mandates Clear Medical Prescriptions for Patient Safety
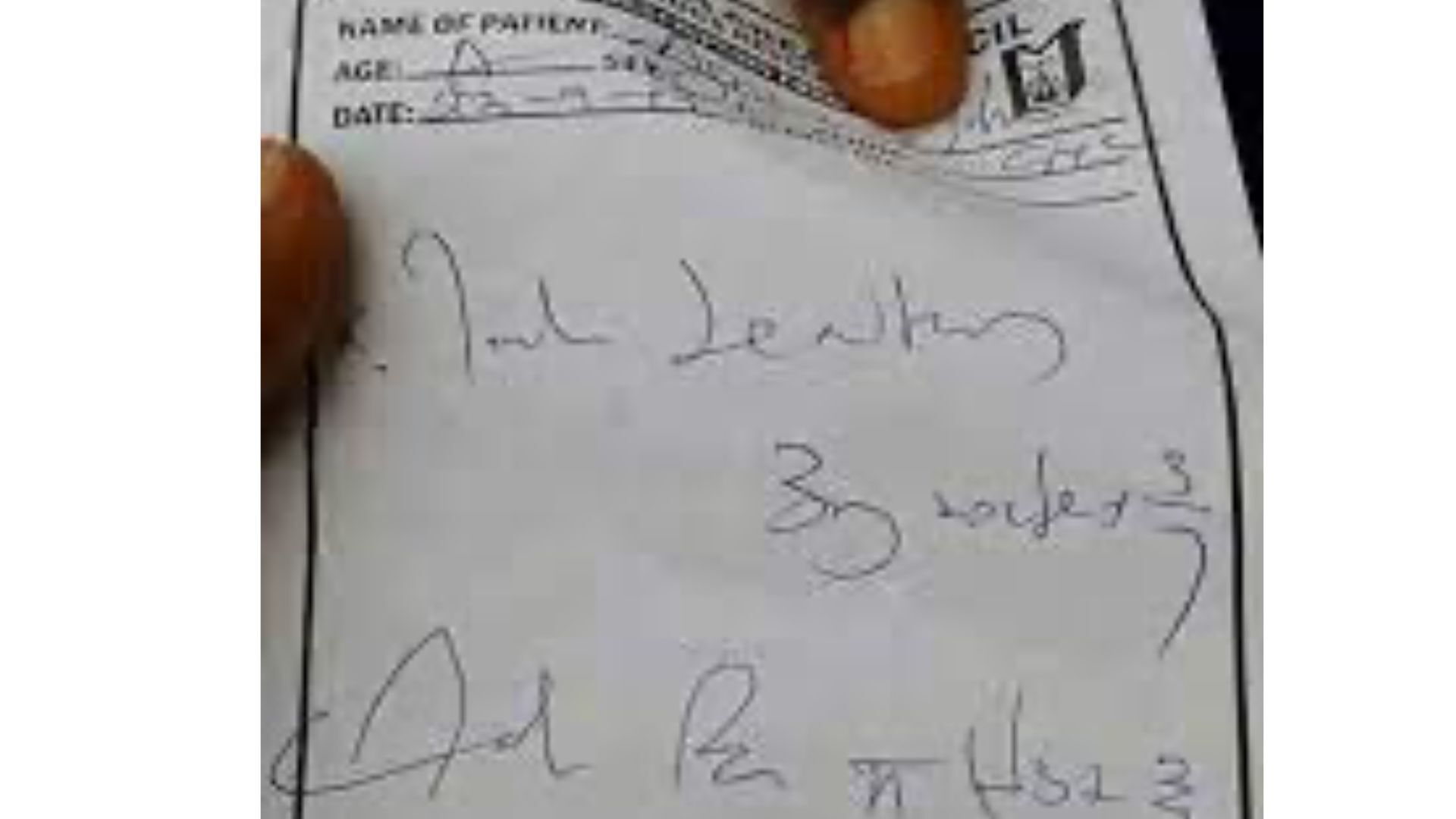
In a significant ruling, the Punjab and Haryana High Court has declared that a “legible medical prescription is a fundamental right.” This observation highlights the potential life-threatening consequences of unclear handwriting by medical practitioners. The ruling stems from a case overseen by Justice Jasgurpreet Singh Puri, who discovered a completely illegible medico-legal report while reviewing charges involving rape, cheating, and forgery.
Justice Puri noted that the unreadability of the report “shook the conscience of this court,” indicating the severe implications of poor handwriting in the medical field. He expressed disbelief that government doctors continue to produce prescriptions that are virtually indecipherable, stating that they could only be read by select chemists. Following this assessment, the court has mandated the introduction of handwriting lessons in medical education and the implementation of digitized prescriptions within a two-year timeframe. In the interim, all medical professionals are required to write prescriptions in clear, capital letters to minimize the risk of errors.
This ruling has brought renewed attention to the longstanding issue of doctors’ poor handwriting, which has become a common topic of humor both in India and internationally. However, medical professionals warn that the consequences of illegible prescriptions are serious. Misdiagnoses, incorrect medications, and even fatalities can result from this widespread issue.
Dr. Dilip Bhanushali, president of the Indian Medical Association (IMA), representing over 330,000 doctors, acknowledged that while many urban practitioners have transitioned to digital prescriptions, the problem remains prevalent in rural and small-town clinics. He stated, “It’s true that many doctors have poor handwriting, but overcrowded hospitals and heavy workloads make it difficult to write neatly.” Dr. Bhanushali emphasized that the IMA has advised its members to comply with the court’s directive by writing prescriptions in bold, legible letters.
The issue of illegible medical prescriptions is not new, as other Indian courts have previously criticized unclear handwriting. Both the Odisha High Court and the Allahabad High Court have raised concerns about “zigzag” or “shabby” prescriptions that are difficult to interpret. Globally, the dangers of illegible prescriptions are well-documented. A report from the Institute of Medicine (IoM) in 1999 estimated that medical errors led to at least 44,000 preventable deaths annually in the United States, with approximately 7,000 linked directly to poor handwriting.
In the United Kingdom, health authorities have recognized that medication errors have caused significant harm, and they believe that electronic prescriptions could reduce mistakes by as much as fifty percent. In contrast, India currently lacks official data on the impact of illegible prescriptions. Nevertheless, numerous cases illustrate the potential dangers, including incidents where patients received incorrect medications due to misinterpretations of doctors’ handwriting. One notable case involved the tragic death of a three-year-old in Noida in 2014 after being administered an incorrect injection.
In response to these alarming situations, Chilukuri Paramathama, a pharmacist from Telangana, filed a public interest petition calling for a ban on handwritten prescriptions. His efforts contributed to the Medical Council of India’s directive in 2016, which mandated that all doctors write generic drug names “legibly and preferably in capital letters.” Despite these measures, pharmacists continue to report challenges in deciphering prescriptions.
Ravindra Khandelwal, CEO of Dhanwantary Pharmacy in Kolkata, noted, “We sometimes have to call doctors for clarification because it’s critical that we dispense the right medicine.”
As the court pushes for digitization and clearer communication, this ruling serves as a crucial reminder that legibility in medical prescriptions is not merely a matter of convenience but a vital component of patient safety. In an age where digital solutions are increasingly available, improving handwriting standards remains an essential task for the medical profession.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoPrivate Funeral Held for Dean Field and His Three Children
-

 Top Stories2 weeks ago
Top Stories2 weeks agoFuneral Planned for Field Siblings After Tragic House Fire
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoNetball New Zealand Stands Down Dame Noeline Taurua for Series
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoTributes Pour In for Lachlan Rofe, Reality Star, Dead at 47
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoNew ‘Maverick’ Chaser Joins Beat the Chasers Season Finale
-

 Sports3 months ago
Sports3 months agoSilver Ferns Legend Laura Langman Criticizes Team’s Attitude
-

 Sports1 month ago
Sports1 month agoEli Katoa Rushed to Hospital After Sideline Incident During Match
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoInvestigation Underway in Tragic Sanson House Fire Involving Family
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoNetball NZ Calls for Respect Amid Dame Taurua’s Standoff
-

 Top Stories2 weeks ago
Top Stories2 weeks agoShock and Grief Follow Tragic Family Deaths in New Zealand
-

 Entertainment3 months ago
Entertainment3 months agoKhloe Kardashian Embraces Innovative Stem Cell Therapy in Mexico
-

 World4 months ago
World4 months agoPolice Arrest Multiple Individuals During Funeral for Zain Taikato-Fox